Shelagh Fogarty 1pm - 4pm
30 November 2020, 15:34
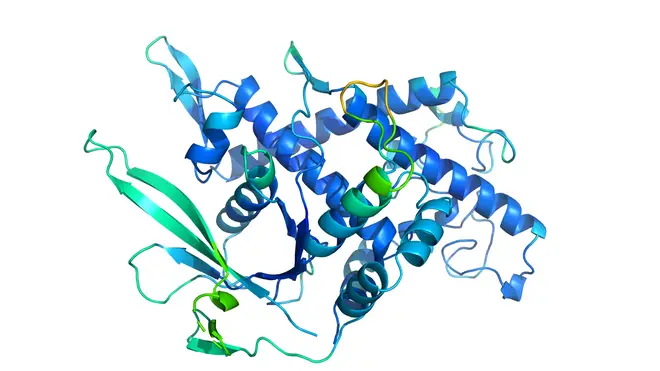
The issue has long been one of biology’s biggest challenges.
A problem dating back five decades may have been cracked by artificial intelligence created in the UK, paving the way for faster development of treatments and drug discoveries.
The so-called “protein folding problem” has long been one of biology’s biggest challenges because there are so many of them and their 3D shapes are difficult to map out.
Almost all diseases, including cancer, dementia and even infectious diseases such as Covid-19, are related to the way these proteins function.
There are 200 million known proteins at present but only a fraction have actually been unfolded to fully understand what they do and how they work.
Google-owned AI lab DeepMind, based in London, says its AlphaFold program has solved the 50-year-old issue and is capable of predicting the shape of many proteins.
They say the system is able to determine highly accurate structures in a matter of days.
DeepMind has worked on the AI project with the 14th Community Wide Experiment on the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (CASP14), a group of scientists who have been looking into the matter since 1994.
“Proteins are extremely complicated molecules, and their precise three-dimensional structure is key to the many roles they perform, for example the insulin that regulates sugar levels in our blood and the antibodies that help us fight infections,” Dr John Moult, chair of CASP14, said.
“Even tiny rearrangements of these vital molecules can have catastrophic effects on our health, so one of the most efficient ways to understand disease and find new treatments is to study the proteins involved.
“There are tens of thousands of human proteins and many billions in other species, including bacteria and viruses, but working out the shape of just one requires expensive equipment and can take years.”
During the latest test, DeepMind said AlphaFold determined the shape of around two-thirds of the proteins with accuracy comparable to laboratory experiments.
But researchers behind the project say there is still more work to be done, including figuring out how multiple proteins form complexes and how they interact with DNA.
DeepMind is planning to submit a paper detailing its system to a peer-reviewed journal to be scrutinised by the wider scientific community.
Professor Venki Ramakrishnan, Nobel Laureate and president of the Royal Society, said: “This computational work represents a stunning advance on the protein-folding problem, a 50-year-old grand challenge in biology.
“It has occurred decades before many people in the field would have predicted.
“It will be exciting to see the many ways in which it will fundamentally change biological research.”